This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose). When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or doesn’t use it effectively, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This can result in serious health complications if not managed properly. But how can you manage diabetes naturally? Let’s explore.
Pathophysiology of Diabetes
At its core, diabetes involves a dysfunction in insulin production and action. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production. In type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, and over time, the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. This insulin resistance is often linked to obesity, physical inactivity, and genetic factors.
Understanding the mechanisms behind these processes is crucial. In type 2 diabetes, for instance, excess fatty acids and inflammatory cytokines can impair insulin signaling pathways, exacerbating insulin resistance. Additionally, the accumulation of visceral fat contributes to hormonal changes that further disrupt glucose metabolism. The interplay between genetics and lifestyle factors creates a complex landscape for diabetes management, highlighting the need for a multifaceted approach.
Dietary Changes
Your diet plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. By making informed food choices, you can maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Focus on Whole Foods
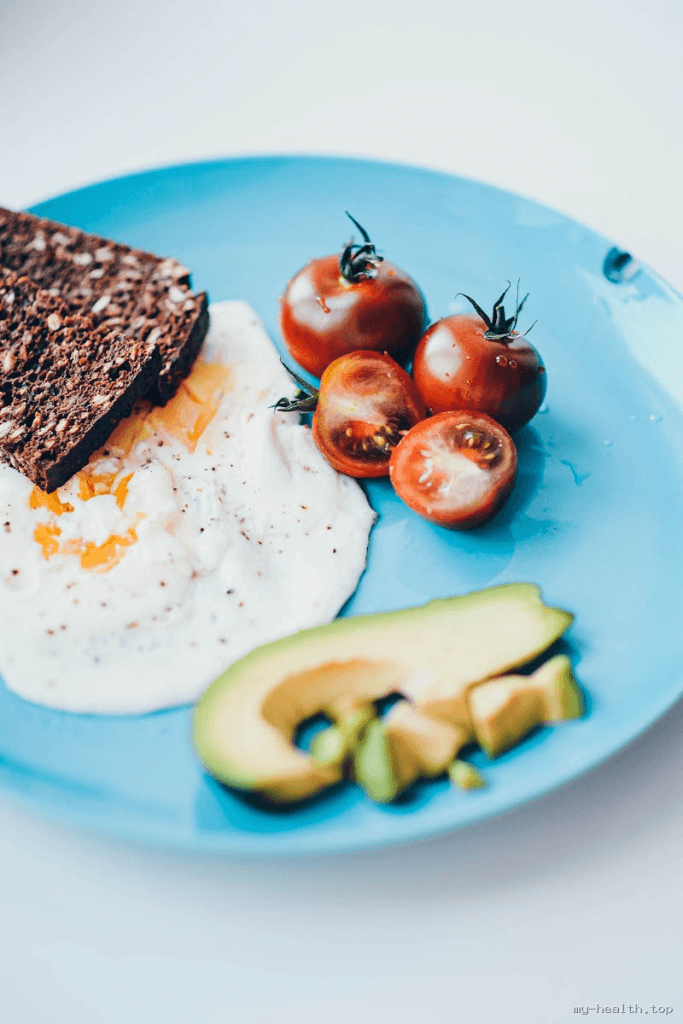
Incorporate whole, unprocessed foods into your meals. Foods rich in fiber, such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, can help regulate blood sugar levels. For example, swapping white rice for quinoa or brown rice can significantly improve your glycemic control. Additionally, legumes like lentils and chickpeas can provide protein and fiber, helping to stabilize blood sugar levels. Aim for a variety of colors on your plate, as different fruits and vegetables offer unique nutrients that support overall health.
Limit Refined Carbohydrates
Refined carbs, found in sugary snacks and white bread, can cause spikes in blood sugar. Instead, choose complex carbohydrates like sweet potatoes and oats, which digest more slowly. This slow digestion results in a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing sudden spikes. Consider meal prepping to ensure you have healthy options readily available, reducing the temptation to reach for processed snacks when hunger strikes.
Healthy Fats and Proteins
Include healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Pairing these with protein can help keep you full and stabilize blood sugar levels. For instance, a snack of almond butter on whole-grain toast is both satisfying and nutritious. Consider adding fatty fish, like salmon, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, known for their anti-inflammatory properties. These healthy fats can also improve heart health, which is particularly important for individuals with diabetes.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is another powerful tool in managing diabetes. It helps improve insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar levels.
Types of Exercise
Incorporate both aerobic exercises (like walking, cycling, or swimming) and strength training (such as weight lifting or resistance bands) into your routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, along with two days of strength training. Research shows that both types of exercise can help reduce HbA1c levels, a key marker of long-term blood sugar control. Consider tracking your physical activity with a wearable device to stay motivated and accountable.
Finding Activities You Enjoy
Choosing activities you love makes it easier to stick with an exercise routine. Consider joining a dance class, hiking with friends, or playing a sport. Enjoyment leads to consistency, which is key to managing diabetes. Setting realistic goals, like walking for 15 minutes after meals, can also help integrate movement into your daily routine. Remember, even small amounts of activity can add up and contribute to better blood sugar control.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels. Learning to manage stress effectively can be a game changer.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress. Even a few minutes each day can make a difference. For example, starting your day with a short meditation can set a positive tone. Research indicates that mindfulness practices can improve emotional well-being and help regulate blood sugar levels. Consider using apps or online resources to guide your practice, making it easier to incorporate into your daily routine.
Sleep Hygiene
Quality sleep is essential for overall health and effective diabetes management. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night. Establish a calming bedtime routine and limit screen time before bed to improve your sleep quality. Poor sleep can lead to insulin resistance and increased cravings for unhealthy foods, creating a vicious cycle. If you struggle with sleep, consider consulting a healthcare provider for strategies to improve your sleep hygiene.
Natural Supplements
Some natural supplements may help manage blood sugar levels, but it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
Popular Options
Supplements like cinnamon, chromium, and alpha-lipoic acid have shown promise in some studies. For instance, cinnamon may improve insulin sensitivity, while chromium can help enhance carbohydrate metabolism. However, the effectiveness of these supplements can vary, and they should be used in conjunction with lifestyle changes rather than as standalone treatments. Always discuss with your healthcare provider to ensure they fit within your overall diabetes management plan.
Patient Vignette
Meet Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Frustrated with her condition, she decided to take control of her health. Sarah began by overhauling her diet, focusing on whole foods and reducing refined sugars. She started walking for 30 minutes each day and incorporated yoga into her routine to manage stress. Within six months, Sarah not only lost weight but also saw significant improvements in her blood sugar levels. Her journey illustrates the power of natural management strategies. Her HbA1c levels dropped from 8.5% to 6.9%, showcasing the potential of lifestyle interventions.
Myth vs. Fact
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| People with diabetes can’t eat carbohydrates. | Carbohydrates can be part of a healthy diet for diabetes; the key is choosing the right types and amounts. |
| Natural remedies can replace medication. | While natural methods can support diabetes management, they should complement, not replace, prescribed medications. |
| All sugars are bad for people with diabetes. | Natural sugars found in fruits can be part of a balanced diet, while added sugars should be limited. |
FAQs About Managing Diabetes Naturally
1. Can I manage diabetes without medication?
Some individuals with type 2 diabetes may manage their condition through lifestyle changes alone. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
2. What foods should I avoid if I have diabetes?
Avoid sugary drinks, processed snacks, and refined carbohydrates. Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
3. How much exercise do I need to manage diabetes?
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training on two or more days.
4. Are there any herbs that help with diabetes?
Some herbs, like cinnamon and bitter melon, have shown potential in managing blood sugar levels. Always consult your doctor before trying new supplements.
5. How can I reduce stress to help manage my diabetes?
Incorporate relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises into your daily routine.
6. Is it safe to use natural supplements for diabetes?
While some natural supplements may help, it’s important to discuss their use with your healthcare provider to avoid interactions with medications.
7. Can stress really affect my blood sugar levels?
Yes, chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which can increase blood sugar levels. Managing stress through mindfulness and relaxation techniques can be beneficial.
8. What is the role of hydration in diabetes management?
Staying hydrated is important as dehydration can lead to increased blood sugar levels. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
9. Can I use essential oils for diabetes management?
While some essential oils may promote relaxation and stress relief, they should not replace conventional treatments for diabetes. Always consult a healthcare provider before use.
10. How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
Monitoring frequency depends on individual treatment plans. Discuss with your healthcare provider to determine the best schedule for your needs.
Key Takeaways
- Dietary changes can significantly impact blood sugar control.
- Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity and overall health.
- Stress management techniques can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Consult healthcare providers before starting any supplements.
- Natural remedies can complement, but not replace, prescribed medications.
References
- American Diabetes Association. (2023). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes–2023. Diabetes Care.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2022). Diabetes Overview.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2023). Diabetes Diet, Eating, & Physical Activity.
- PubMed. (2023). The Role of Diet in Diabetes Management.
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2021). Diabetes.
- UpToDate. (2023). Lifestyle Management in Diabetes.






Post a comment