This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Understanding Cancer Prevention
Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, but many cases are preventable. The latest research highlights various strategies that can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer. But what exactly are these strategies, and how can you incorporate them into your daily life? Understanding the underlying mechanisms of cancer development can empower you to make informed decisions about your health.
Pathophysiology of Cancer
Cancer arises from genetic mutations that lead to uncontrolled cell growth and division. These mutations can be influenced by various factors, including environmental exposures, lifestyle choices, and inherited genetic predispositions. For instance, carcinogens such as tobacco smoke or excessive UV radiation can damage DNA, leading to mutations that may initiate cancer development. The body has mechanisms to repair DNA, but when these systems fail, cancer can emerge.
At a cellular level, cancer cells often exhibit altered metabolism, known as the Warburg effect, where they rely on glycolysis for energy production even in the presence of oxygen. This shift not only supports rapid cell division but also creates an acidic microenvironment that promotes tumor growth and metastasis. Understanding these mechanisms underscores the importance of lifestyle choices in cancer prevention.
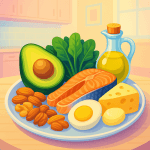
Diet: Fueling Your Body for Health
Recent studies emphasize the role of diet in cancer prevention. A 2020 study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can lower the risk of several types of cancer. These foods are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are linked to cancer development.
Key Foods to Include
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a variety of colors on your plate. Berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli are particularly beneficial due to their high levels of phytochemicals. For example, cruciferous vegetables contain sulforaphane, which has been shown to inhibit cancer cell growth.
- Whole Grains: Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and oats provide essential nutrients and fiber, which can aid in digestion and help regulate blood sugar levels. Fiber is crucial as it promotes a healthy gut microbiome, which is increasingly recognized for its role in cancer prevention.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources like olive oil, avocados, and nuts to support overall health and reduce inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, have anti-inflammatory properties that may help lower cancer risk.
Foods to Limit
Processed foods, red meats, and sugary drinks have been linked to increased cancer risk. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends limiting these items in your diet. For example, processed meats have been classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, meaning there is sufficient evidence to conclude that they can cause cancer. Additionally, high sugar intake can lead to obesity, which is a significant risk factor for various cancers.
Physical Activity: Move More, Live Longer
Regular physical activity is another cornerstone of cancer prevention. According to the CDC, engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly can lower your risk of breast, colon, and other cancers. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces inflammation, and improves immune function, all of which play a role in cancer prevention.
Finding Your Fit
Incorporate exercises you enjoy, whether it’s walking, cycling, or dancing. The key is consistency. Consider joining a local sports team or a fitness class to stay motivated. Setting small, achievable goals can also help keep you on track. For instance, aim to walk 10,000 steps a day or participate in a charity run. Additionally, strength training exercises can help build muscle and improve metabolic health, further reducing cancer risk.
Avoiding Tobacco and Limiting Alcohol
Tobacco use is the leading cause of cancer and cancer deaths. The CDC reports that smoking is linked to various cancers, including lung, throat, and mouth cancer. Quitting smoking can drastically reduce your risk. Even those who have smoked for years can benefit from cessation, as the body begins to heal shortly after quitting. For example, within just a year of quitting, the risk of heart disease decreases significantly.
Alcohol Consumption
Limiting alcohol intake is also crucial. The American Cancer Society recommends no more than one drink per day for women and two for men. Excessive alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk of several cancers, including breast and liver cancer. It’s important to be mindful of the type and amount of alcohol consumed; for example, beer and spirits can have different effects on health compared to wine. Consider substituting alcoholic drinks with non-alcoholic options like sparkling water or herbal teas to reduce intake.
Regular Screenings: Catching Cancer Early
Screening tests can detect cancer early when it’s most treatable. The American Cancer Society provides guidelines for various screenings, including mammograms, colonoscopies, and Pap tests. Early detection significantly improves survival rates, as many cancers are more treatable when caught in their initial stages.
Know Your Risk
Discuss your family history and personal risk factors with your healthcare provider to determine which screenings are appropriate for you. For instance, individuals with a family history of breast cancer may benefit from earlier or more frequent mammograms. Additionally, genetic testing may be recommended for those with a strong family history, allowing for personalized prevention strategies.
Vaccinations: Protecting Against Cancer
Certain vaccines can prevent cancers caused by viruses. The HPV vaccine, for instance, can significantly reduce the risk of cervical and other cancers. The CDC recommends the HPV vaccine for preteens and young adults. Additionally, the hepatitis B vaccine can help prevent liver cancer. Vaccination is a proactive step that can lead to long-term health benefits, especially in younger populations.
Patient Vignette: Sarah’s Journey to Prevention
Sarah, a 45-year-old woman, was concerned about her family history of breast cancer. After consulting with her doctor, she adopted a healthier lifestyle. She began exercising regularly, switched to a plant-based diet, and quit smoking. After a year, Sarah felt more energetic and was proud to have reduced her cancer risk. Her story illustrates how proactive changes can lead to significant health benefits. Sarah also scheduled regular screenings, which provided her with peace of mind and ensured her health was monitored closely.
Frequently Asked Questions
What lifestyle changes can help prevent cancer?
Incorporating a balanced diet, regular exercise, avoiding tobacco, limiting alcohol, and attending screenings can significantly lower your cancer risk.
How does diet influence cancer risk?
A diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients that help protect against cancer. These foods can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are linked to cancer development.
Are there vaccines for cancer prevention?
Yes, vaccines like the HPV vaccine can prevent cancers caused by certain viruses. The hepatitis B vaccine is also important in preventing liver cancer.
How often should I get screened for cancer?
Screening frequency depends on your age, gender, and risk factors. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations. For example, women should start cervical cancer screenings at age 21, while colon cancer screenings generally begin at age 45.
Can I reduce my risk of cancer if I have a family history?
Yes, while family history can increase risk, lifestyle changes can still significantly reduce your overall risk. Engaging in healthy habits can mitigate some genetic predispositions.
Myth vs. Fact
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| All cancers are hereditary. | While genetics play a role, many cancers are influenced by lifestyle choices and environmental factors. |
| Only older adults get cancer. | Cancer can affect individuals of any age, though risk increases with age. |
| Organic foods are the only way to prevent cancer. | While organic foods can be part of a healthy diet, a balanced diet with a variety of foods is more important. |
| Eating sugar causes cancer. | While excessive sugar intake can lead to obesity, which is a risk factor for cancer, sugar itself does not directly cause cancer. |
| Vitamins can cure cancer. | While certain vitamins can support overall health, they should not be viewed as a cure for cancer. Treatment should always be guided by healthcare professionals. |
Key Takeaways
- Adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables can lower cancer risk.
- Regular physical activity is essential for cancer prevention.
- Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol consumption are crucial steps.
- Regular screenings can help catch cancer early when it is most treatable.
- Vaccinations like the HPV vaccine can prevent certain types of cancer.
References
- World Health Organization. (2020). Cancer prevention. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer
- American Cancer Society. (2022). Cancer prevention and early detection. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Physical activity and cancer prevention. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/dcpc/resources/features/physicalactivity/index.htm
- National Cancer Institute. (2023). Diet, nutrition, and cancer prevention. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/diet
- PubMed. (2020). Diet and cancer prevention: A review. Journal of Clinical Oncology.
- UpToDate. (2023). Cancer prevention strategies. Retrieved from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/cancer-prevention-strategies





Post a comment