This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Understanding Diabetes Management
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose). Managing diabetes effectively requires a multifaceted approach, particularly focusing on nutrition and lifestyle changes. But how do you start? What specific changes can make a difference? Understanding the underlying mechanisms of diabetes can empower you to take control of your health.
The Pathophysiology of Diabetes
Diabetes primarily involves issues with insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin due to autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells. In contrast, type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. Over time, this can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, resulting in various complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular diseases.
Interestingly, the pathophysiology of diabetes also involves the liver, muscles, and fat tissue. For instance, in insulin resistance, the liver may produce excess glucose, while muscle and fat cells fail to take up glucose efficiently. This complex interplay leads to a cycle of increasing blood sugar levels, which can be exacerbated by factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and poor dietary choices (American Diabetes Association, 2023).
The Role of Nutrition in Diabetes Management
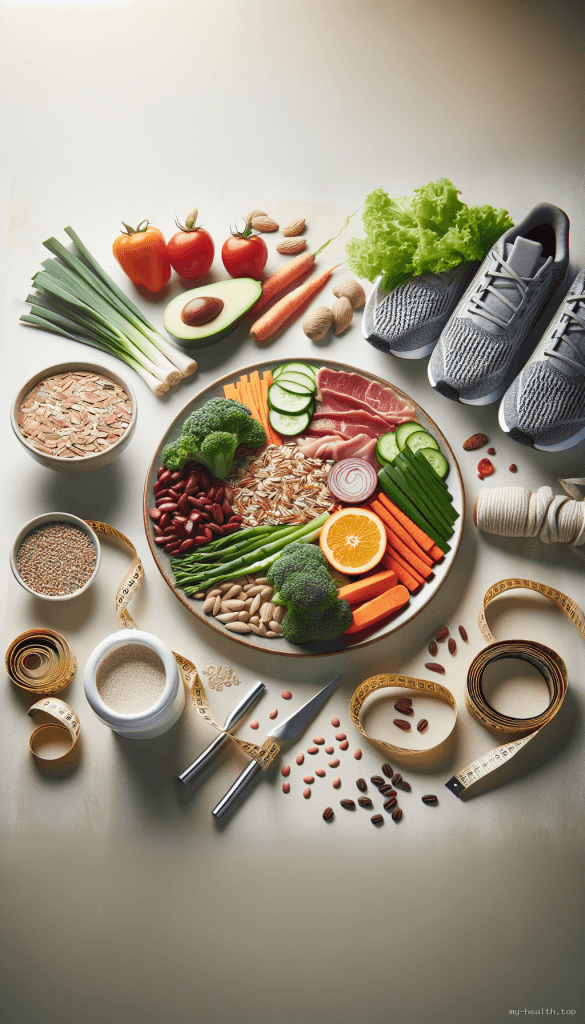
Nutrition plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. A well-balanced diet helps control blood sugar levels, reduces the risk of complications, and promotes overall health. But what specific dietary choices can you make to support your health?
1. Emphasize Whole Foods
Whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, should form the cornerstone of your diet. These foods are rich in nutrients and fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar levels. For instance, incorporating leafy greens like spinach and kale can provide essential vitamins while keeping carbohydrate intake low. Aim for a colorful plate—different colors often represent different nutrients.
2. Monitor Carbohydrate Intake
Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. Learning to count carbs can be a game-changer. Aim for complex carbohydrates, such as brown rice and quinoa, over simple sugars found in sweets and sodas. Using tools like carbohydrate counting apps can simplify this process. Remember, not all carbs are equal; prioritize fiber-rich options that digest slowly and help maintain stable blood sugar levels. The glycemic index (GI) can also be a useful tool; foods with a low GI are absorbed more slowly, leading to gradual increases in blood sugar (World Health Organization, 2020).
3. Choose Healthy Fats
Not all fats are created equal. Focus on healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. These fats can improve heart health, which is especially important for those with diabetes, as they are at a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, can also reduce inflammation and support heart health.
Making Lifestyle Changes
In addition to nutrition, lifestyle changes can significantly impact diabetes management. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Regular Physical Activity
Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking or cycling. Strength training exercises can also be beneficial, as they help build muscle mass, which can improve glucose uptake. Even small changes, like taking the stairs instead of the elevator, can contribute to your overall activity level. Engaging in activities you enjoy can make it easier to stay active.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Weight management is crucial for diabetes control. Losing even a small percentage of your body weight can enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. Consider working with a registered dietitian to create a personalized weight loss plan. Tracking your food intake and physical activity can also provide valuable insights into your progress. Remember, weight loss is a gradual process; setting realistic goals can help maintain motivation.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can be beneficial. Finding time for hobbies or relaxation can also help alleviate stress. Additionally, consider journaling or talking to a friend about your feelings to help process stressors. Understanding how stress impacts your body can empower you to take proactive steps to manage it.
Monitoring and Self-Management
Self-monitoring is essential in diabetes management. Regularly checking your blood sugar levels can help you understand how your diet and lifestyle choices affect your body. Keep a log of your readings to identify patterns and discuss them with your healthcare provider. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are also an option for real-time tracking and can provide valuable data for managing diabetes. These devices can help you see how different foods and activities impact your blood sugar, allowing for more informed decisions.
Patient Vignette
Meet Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Initially overwhelmed, she began by consulting a registered dietitian who guided her in creating a balanced meal plan. Sarah started incorporating more whole foods and reduced her intake of processed sugars. Alongside dietary changes, she began walking for 30 minutes daily. Over six months, Sarah lost 15 pounds and saw her blood sugar levels stabilize, significantly improving her energy levels and overall well-being. She also reported feeling more in control of her health, which enhanced her motivation to maintain these changes. Sarah’s story highlights the importance of individualized care and the positive impact of small, sustainable changes.
Myth vs. Fact
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| People with diabetes cannot eat sweets. | Moderation is key. Small portions of sweets can be included in a balanced diet. |
| Carbohydrates should be completely avoided. | Healthy carbohydrates are essential for energy. Focus on whole grains and fiber-rich foods. |
| Exercise is not necessary if you manage your diet. | Regular physical activity is vital for overall health and blood sugar control. |
| All fats are bad for diabetes. | Healthy fats can support heart health and improve insulin sensitivity. |
| Diabetes is solely a dietary problem. | Diabetes management involves a combination of diet, exercise, monitoring, and sometimes medication. |
FAQs about Managing Diabetes
1. What are the best foods for managing diabetes?
Foods high in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats, like vegetables, whole grains, and fish, are excellent choices.
2. How often should I check my blood sugar?
This depends on your treatment plan. Some may need to check multiple times a day, while others may do so less frequently. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
3. Can I drink alcohol if I have diabetes?
Moderate alcohol consumption can be safe for some people with diabetes, but it’s essential to monitor blood sugar levels and consult your doctor.
4. How can I lose weight effectively with diabetes?
Focus on a balanced diet and regular exercise. Working with a healthcare professional can help create a tailored weight loss plan.
5. Is it safe to follow a low-carb diet?
Many people with diabetes benefit from a low-carb diet, but it’s essential to ensure you’re still getting adequate nutrition. Discuss this with a healthcare provider.
6. How can I manage diabetes when eating out?
Plan ahead by checking menus online, choosing grilled or baked options, and asking for dressings or sauces on the side. Portion control is also key.
7. What should I do if I experience low blood sugar?
Always carry a source of fast-acting sugar, such as glucose tablets or juice. If you experience symptoms like dizziness or confusion, consume 15 grams of carbohydrates and recheck your blood sugar after 15 minutes.
Key Takeaways
- Nutrition is key in managing diabetes; focus on whole foods and healthy fats.
- Monitor carbohydrate intake to control blood sugar levels effectively.
- Regular physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity and aids weight management.
- Stress management techniques can positively impact blood sugar levels.
- Self-monitoring blood sugar helps identify effective dietary and lifestyle changes.
References
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes–2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(Supplement 1):S1-S2.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diabetes and Nutrition. 2022.
- World Health Organization. Healthy diet. 2020.
- National Health Service. Diabetes and diet: What to eat. 2022.
- PubMed. The Role of Diet in Diabetes Management. 2023.
- UpToDate. Lifestyle management of type 2 diabetes. 2023.






Post a comment